马贵军课题组介绍
| 课题组长(PI) |
|
Prof. Guijun Ma received his BEng from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Lanzhou University in 2002. He then completed his PhD on photocatalytic splitting of H2S at Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics under the supervision of Prof. Can Li. Later, he worked as a postdoctoral researcher in the groups of Prof. Kazunari Domen at the University of Tokyo and Prof. Kazuhiro Takanabe at KAUST, respectively. In 2009, he was appointed as the Principal Researcher at ARPChem, the University of Tokyo, working on photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Prof. Ma joined the School of Physical Science and Technology of ShanghaiTech University in 2017 as a principal investigator. The main research focus of his group is developing novel inorganic materials for efficient solar water splitting systems. Prof. Guijun Ma has secured competitive research funding from both the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission through their General Programs. He was selected for the prestigious Top Young Talents Project under Shanghai’s Oriental Talents Program. As an active member of the academic community, Prof. Guijun Ma serves as a Youth Committee Member on the Photochemistry Committee of the Chinese Renewable Energy Society. His teaching portfolio includes delivering core courses in Electrochemistry and Principles of Catalysis to both undergraduate and graduate students. |
| 研究简介(Research) |
|
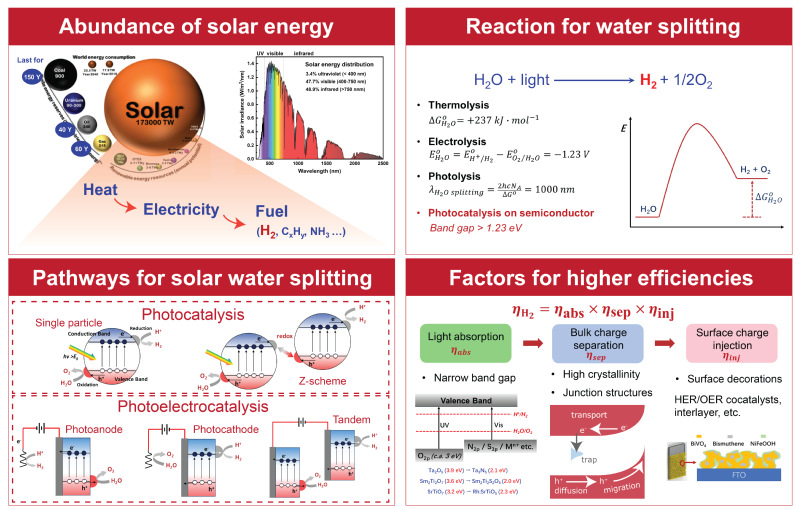
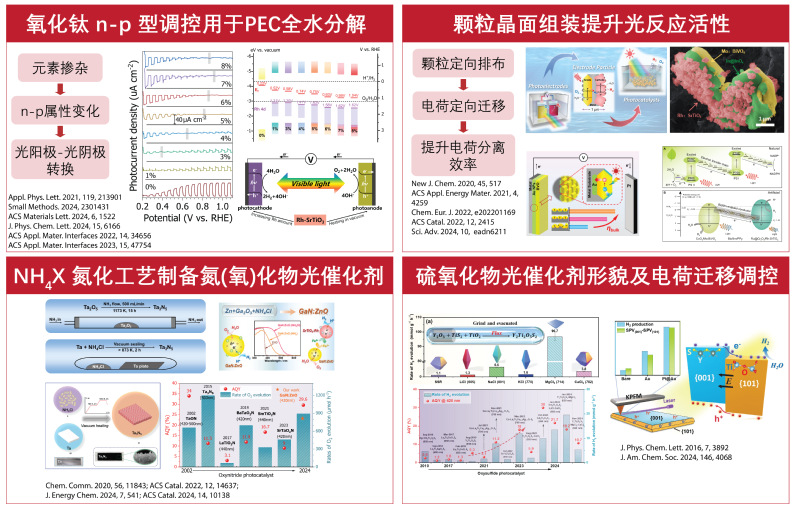
Our group aims at developing new photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting materials and devices, which use sunlight as energy input to sustainably produce H2 as clean fuel. To make it commercially viable, we must consider not only elevating its energy conversion efficiency, but also the extending the stability and reducing the costs. Having these factors in mind, we find that transition metal oxides, oxysulfides and (oxy)nitrides with visible responses are candidates with great prospect. At the moment, the state-of-the-art energy conversion efficiency is still rather low, but our preceding research has shown there is plenty of room for improvement with careful control of crystallinity, morphology and surface treatment. The main research interests of our group are: 1. Developing cost effective synthetic methods for high performance transition metal oxysulfides and (oxy)nitrides for H2 and O2 evolution reactions. 2. Realizing high overall water splitting efficiency with electrode- or powder-based Z-scheme systems. 3. Gaining mechanistic understanding of photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical processes with advanced characterizations, such as intensity modulated photocurrent spectroscopy and surface photovoltage spectroscopy
|
主要从事开发具有可见光响应的氧化物、硫(氧)化物及氮(氧)化物无机半导体材料,通过结晶优化,形貌控制以及表面修饰等实验手段 将这一材料应用于太阳能光催化及光电化学分解水制氢反应,在注重催化剂效率的同时,兼顾成本控制及可行性分析,致力于开发出具有 一定工业示范前景的光催化材料和反应。 主要方向: (1)开发低价、高效的氧硫(氮)化物光催化材料的合成方法; (2)基于Z-体系理念实现光催化及光电化学分解水全反应; (3)无机半导体光催化分解水反应机理探索 |
| 发表文章(Publications) |
|
76.“A Rhodium-Doped PbTiO3 Photocathode Applicable to Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting”B. Zhang, J. Zhang, K. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Xu, K. Shi, Z. Zhang, J. Zhang* and G. Ma*, ACS Catal, 2026.
75.“A Ta3N5/BN composite for enhanced photocatalytic water splitting”Y. Xu, H. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, M. Liu, X. Tao, J. Zhang* and G. Ma*,Chemical Communications,2025.
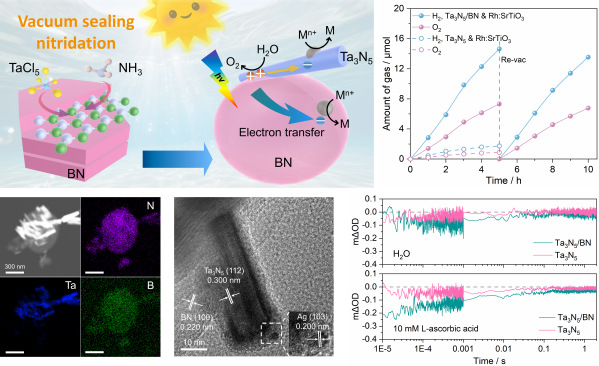
本文采用BN作为支撑载体生长Ta3N5晶体,制备了分布均匀的Ta3N5/BN纳米复合结构光催化剂。Ta3N5/BN表现出与块体Ta3N5相当的高效可见光吸收,同时光化学贵金属沉积实验与XPS能谱分析显现出光生载流子在Ta3N5与BN基底之间转移的现象,结合TAS验证了复合结构显著提升了Ta3N5的电荷分离效率。基于电子相互作用的提升,实现了高效光催化水氧化反应与直接型Z-scheme全水分解反应的构建。
74.“Oxysulfide Photocatalyst Breaking the 60% Quantum Efficiency Barrier for Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Production from Water”J. Zhang, Y. Xu, H. Wang, M. Liu, K. Shi, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, K. Liu, J. Zhang and G. Ma*,Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy,2025.
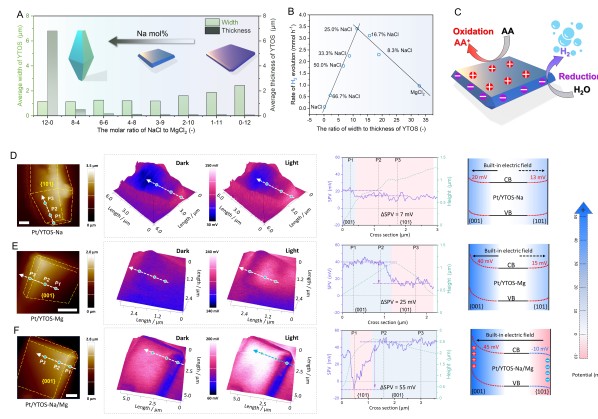
光催化分解水是将太阳能转化为氢能的理想途径,高效光催化剂需具有宽光谱吸收及快速电子-空穴分离的特性。本研究以具有可见光响应能力且化学稳定性优异的氧硫化物为基础材料,创新采用熔盐助熔法降低材料合成过程中的扩散能垒,成功制备出片状十面体结构的YTOS颗粒。通过表面光电压显微镜,精准观测到不同晶面的电荷种类与光电压大小,进而清晰解析晶面间的电位差与内建电场分布特征,为YTOS材料高效的电荷分离特性提供直接实验证据
doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2025.125861
73.“A rod-shaped Bi2MoO6/Bi14MoO24 homoelemental heterojunction for efficient degradation of tetracycline” J. Yi*, X. Xiao, Z. Chen, Z. Ou, S. Liang, Z. Huang, Z. Liu, D. Li*, J. Zhang, K. Liu, G. Ma, C. Yu*, Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2025.
doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2025.182717
72.“On-Site Growth of a TaON Nanoshell on ZrO2 Particles for Photocatalytic Water Splitting” Y. Xu, H. Wang, Y. Qiu, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, K. Shi, X. Tao, Z. Zhang, M. Liu, C. Xu,*and G. Ma*,ACS. Applied. Materials & Interfaces 2025.
pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsami.5c12427
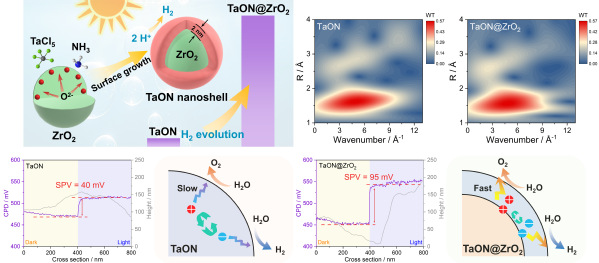
本文创新性利用ZrO2纳米颗粒作为O2–离子供体制备厚度可控的超薄TaON纳米壳。ZrO2载体提供的O2–离子定向表面迁移诱导了TaON纳米壳均匀生成,同时精细结构分析表明TaON纳米壳与块体TaON具有高结晶度,降低的载流子迁移距离大幅提升载流子分离效率与光催化活性
71.“Facet-oriented surface modification for enhancing photocatalytic hydrogen production on Sm2Ti2O5S2nanosheets, Z. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Wang, M. Liu, Y. Xu, K. Liu, B. Zhang, K. Shi, J. Zhang*, G. Ma*, Chin. J. Catal.2025,74,341–351.
doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(25)64731-0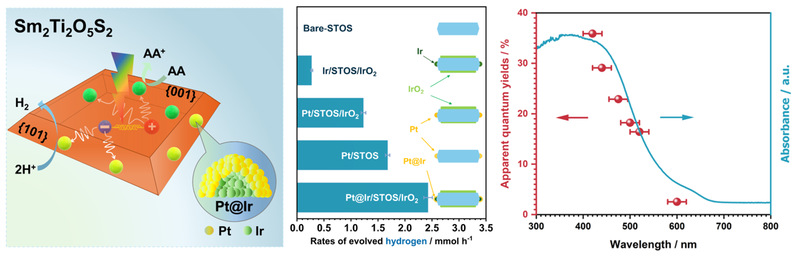
本工作首次揭示了Sm2Ti2O5S2纳米片的各向异性电荷迁移特性。通过在特定晶面原位选择性沉积Pt@Ir和IrO2协同助催化剂,显著提高了其光催化产氢活性,使表观量子效率(AQY)提升至35.9%。此外,以Sm2Ti2O5S2作为高效析氢光催化剂,实现了Z型体系的整体水分解反应。
70.“Dynamic Probing of Intermediates in (Photo)electrocatalytic Reactions Using Frequency-Resolved Excitation-Modulated Absorption Spectroscopy”J. Zhang*, M. Liu, H.Wang, S.Guan and G.Ma*, J. Am. Chem. Soc. Au, 2025.
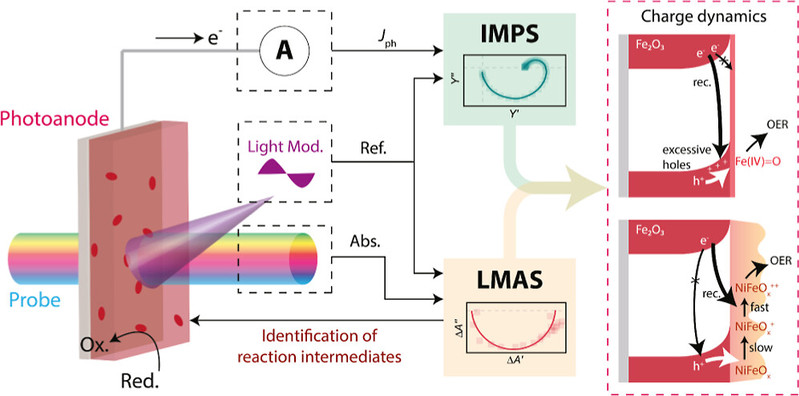
课题组利用自主开发的激励调制(光强、电压)吸收光谱,原位动态检测出Fe2O3-NiFeOx复合光阳极的中间物种以及特征响应时间。实验结果表明中间物种的氧化还原速率为决定复合光阳极性能的关键因素。该成果不但为复合光阳极设计提供了新思路,还为复杂光电化学机理的探究提供了新型探索范式。
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacsau.5c00131
69.“Etched BiVO4 photocatalyst with charge separation efficiency exceeding 90%” S. Wang, C. Li, Y. Qi, J. Zhang, N. Wang, M. Liu, B. Zhang, X. Cai, H. Zhang, Su-huai. Wei, G. Ma*, J. Yang*, S. Chen* and F. Zhang*, Nature Communications,2025, 16:3776.
doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59076-8
68.“Preparation and Insight of [010]-Orientated BiVO4 PlanarPhotoanode via One-Step Pyrolysis for SignificantlyPromoted Charge Separation and Water Oxidation”S. Zhang, J. Zhang, N. Yang, Y. Xiao, R. Wang, Y. Bao,G. Ma, S. Jin, and F. Zhang* ,Adv. Sci. 2025,2416474.
doi.org/10.1002/advs.202416474
67.“Modulation of the Photo-response of SrTiO3: Insights of Surface Defect on Solid Oxide Photoelectrochemical Cell” L. Wang, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, G. Ma* and N. Yang*,J. Mater. Chem. A, 2025.
66.“Boronium-Based Polythiophene Networks: Synthesis,Characterization, and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Property”X. Han, B. Zhang, H. Chen, M. Peng, C. Xue, H. Liu, G. Ma* and Y. Ren*,Macromolecules,2025, 58, 2, 1117–1125.
doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.4c02150
65.“Furan-Based HTCC/In2S3 Heterojunction Achieves Fast ChargeSeparation To Boost the Photocatalytic Generation of H2O2 in PureWater” X. Tang, C. Yu*, J. Zhang, K. Liu, D. Zeng, F. Li, F. Li, G. Ma, Y. Jiang and Y. Zhu*,ACS Catal,2024,14,16245-16255.
doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.4c04341
64.“Studies on Ultrafast Photocarrier Recombination Mechanisms of the Rh-Doped BaTiO3 Photocatalyst” Z. Lv, H. Kuang, G. Ma, J. Chen and R. Li*,J. Phys. Chem. C,2024.
doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c02565
63.“Synthesis of Highly Active GaN:ZnO Photocatalysts Applicable to Z-Scheme Overall Water Splitting Systems” K. Liu, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, Y. Xu, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, K. Shi, N. Wang, S. Chen and G. Ma*,ACS Catal, 2024, 14,10138–10147.
doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.4c02172
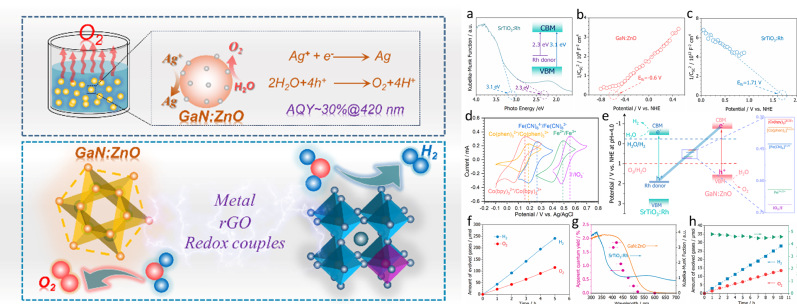
本工作在真空封管氮化工艺的基础上通过调控卤化铵和金属Zn的比例制备了高分散性、界面缺陷少以及结晶度好的GaN:ZnO催化剂颗粒。在牺牲试剂存在的情况下,GaN:ZnO在420nm处的表观的量子效率(AQY)达到30%。同时,GaN:ZnO还作为一种优异的析氧光催化剂构建了三类Z-scheme全水分解体系。包括基于p-n耦合的无偏压光电化学水分解、直接Z-scheme以及氧化还原离子电对的离子型Z-scheme水分解。该研究首次证明GaN:ZnO可以作为一种普适性的析氧光催化剂应用各类Z-scheme全水分解中。
62“Conformal and conductive biofilm-bridged artificialZ-scheme system for visible light–driven overallwater splitting” X. Wang, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, X. Jiang, K. Liu, H. Wang, X. Yuan, H. Xu, Y. Zheng, G. Ma*, C. Zhong*,Science Advances, 2024.
doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn6211
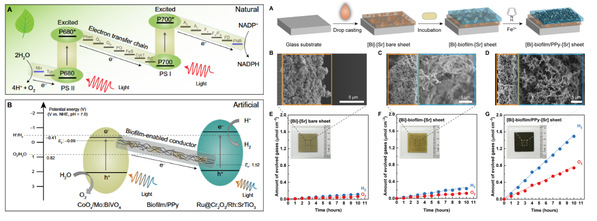
本工作依托工程化的大肠杆菌生物被膜,基于吡咯原位聚合的方式开发了共形贴附导电生物被膜,并通过逐层沉积法制备了有机-无机半人工杂化Z-scheme(Mo:BiVO4-biofilm/Ppy-Rh:SrTiO3),该涂层具备自支撑性,颗粒间接触紧密,展现了优异的光催化全解水性能。同时,优化后的体系拥有100h以上的运行稳定性以及对常压的耐受性,具有规模化生产的潜力。本工作实现了活体能源材料在可持续清洁能源方面的应用,并对生物整合相关的的器件系统设计有重要的参考意义
61.“A Visible Light-Responsive TiO2 Photocathode Achieved by a RhDopant” Y. Tang, K. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Wang, H. Wang, M. Liu, J. Zhang* and G. Ma*,J. Phys. Chem. Lett, 2024, 15, 6166-6173.
doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00910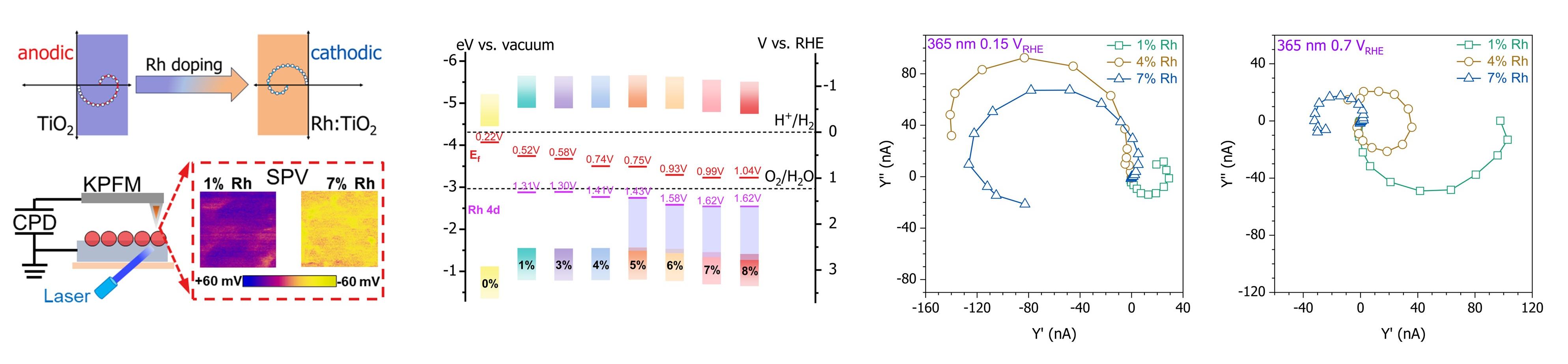
本文展示了金红石型TiO2作为光电阴极的潜力,通过Rh的掺杂其可见光吸收拓展至640 nm。通过Mott-Schottky曲线和开尔文探针力显微镜证实,掺杂使TiO2从n型半导体转变为p型半导体。利用物理和光电化学分析进一步揭示了Rh掺杂机制与掺杂浓度有关。本工作阐明了Rh掺杂在调节TiO2光电化学行为中的作用,为太阳能转换提供了一种有前景的光电阴极材料。
60.“Orienting Charge Migration in TiO2 Photocathode through Directionally Distributed Rh Dopant” M. Liu, J .Zhang*, K. Liu, Z. Nie, K. Hu, J. Zhang, Y. Chang, B. Zhang, N. Yang* and G. Ma*,ACS Materials Lett, 2024, 6, 1522-1531.
doi.org/10.1021/acsmaterialslett.4c00061
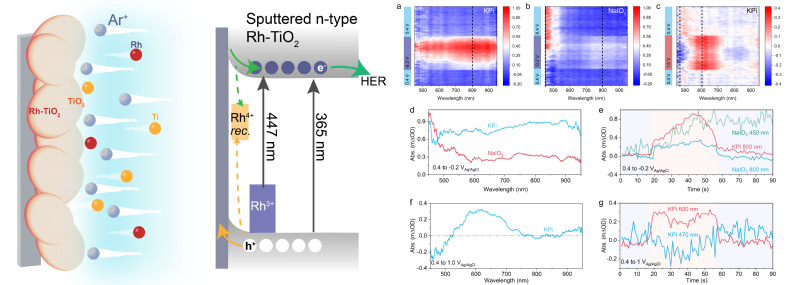
本工作制备了一种定向Rh梯度掺杂金红石TiO2光电极,促使光生载流子有序迁移,实现Rh-TiO2光阳极到光阴极的转变。利用强度调制光电流光谱 (IMPS) 和光谱电化学(SEC)揭示了掺杂剂Rh3+/Rh4+在电荷动力学中的不同作用。在这项工作中定向掺杂实现了光生电子-空穴分离,并为半导体光阴极的制备提供了新途径。
59. “Synthesis of Narrow Bandgap Gallium Zinc Nitride Oxide Solid Solutions for Photocatalytic Water Splitting under Visible Light” N. Iwasa, Zh. Teng, G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen*, Chemistry of Materials, 2024,146,4068 - 4077.
doi/10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c03262
58. “NH4Cl-assisted synthesis of TaON nanoparticle applied to photocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution from water” Y. Xu, K. Liu, J. Zhang, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, K. Shi, H. Wang, G. Ma*, Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024,7,541-550.
doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2024.02.051
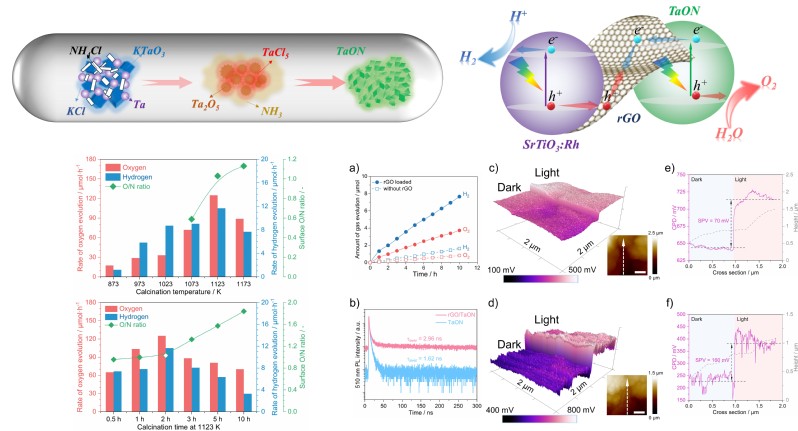
本文首次采用NH4Cl作为氮源合成窄带隙TaON纳米颗粒,420 nm单色光照射下的析氧反应可实现6.4%的表观量子效率,并通过还原氧化石墨烯作为固体电子介质成功实现了全固态Z体系可见光驱动的全水分解。这一方法拓展了真空氮化工艺在制备窄带隙氧氮化物半导体材料方面的应用,为开发高效太阳能光催化剂提供了一种新思路。
57. “The Role of Cobalt-Based Cocatalysts on BiVO4 for Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation” Z.Nie, B.Zhang, J.Zhang, K.Hu, G.Ma*, N.Yang*, ChemCatChem, 2024, e202301683
doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202301683
56. “Anisotropic Charge Migration on Perovskite Oxysulfide for Boosting Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting” J. Zhang, K.Liu, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, M. Liu, Y. Xu, K. Shi, H. Wang, Z. Zhang, P. Zhou*, and G. Ma*, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024. 146, 6, 4068–4077

合成兼具宽光谱吸收和高效电荷分离能力的光催化剂对实现高效太阳能转换至关重要。我们采用熔盐法合成了高结晶度和高比表面积的YTOS纳米片,并且通过析氢/析氧助催化剂的选择性沉积首次发现窄带隙钙钛矿氧硫化物Y2Ti2O5S2具有各向异性电荷迁移特性。同时,利用密度泛函理论(DFT)计算阐明了YTOS中晶面导向电荷迁移的原因是YTOS的{101}和{001}晶面之间存在能带能级差,证明了II型表面异质结的形成,从而促进了有效的载流子分离。结合原位表面光电压显微镜(KPFM)证实了内建电场强度与光催化产氢活性的构效关系。最终,通过助催化剂的晶面工程实现了高效的光催化全水分解。
55. “Efficient overall water splitting of a suspended photocatalyst boosted by metal-support interaction” Y. Qi, B. Zhang, G. Zhang, Z. Zheng, T. Xie, S. Chen, G. Ma, C. Li, K. Domen, and F. Zhang*, Joule,2024, 8, 193-203.
doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2023.12.005
54. “Probing Intra-Gap States Mediated Charge Dynamics of Rh-Doped Rutile TiO2 Photocatalyst by Light-Modulated Photocurrent Spectroscopies” J. Zhang, M. Liu, Y. Tang, G. Qian, G. Ma*, Small Methods, 2024.
doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202301431
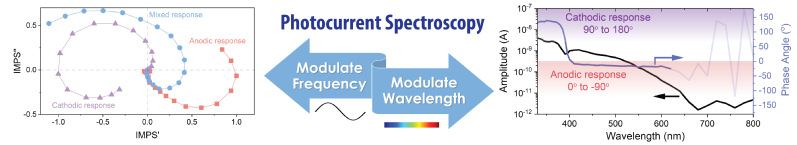
光电流谱学是一类探测半导体光生电荷动力学过程的有效手段,为此我们开发了高灵敏度亚带隙激发强度调制光流谱(IMPS)技术,并结合交流光电流谱表征,探究了Rh掺杂金红石TiO2材料内双光子激发机制,且首次发现一种新型表面电荷传输路径。
53. “Rhodium-Doped Barium Titanate Perovskite as a Stable p-Type Photocathode in Solar Water Splitting” K. Shi, B. Zhang, K. Liu, J. Zhang*, and G. Ma*, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 40, 47754–47763.
doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c09635

Rh:BaTiO3因具有三种主要优势是一种有前景的光阴极材料:(1)吸收可见光以更好地捕获太阳能;(2)高达1.0 V ( vs. RHE) 的起始电位,用于构建高效且无偏置的p-n共轭PEC系统;(3)具有长期光稳定性,适用于实际应用。通过对SPS振幅和相位谱的全面分析,我们揭示了较高的Rh掺杂水平逐渐降低了电极材料的费米能级,并使BaTiO3从n型半导体调制为p型半导体成为可能。该项研究提出了开发实用光阴极的策略,并将SPS描述为调查半导体类型转换的有用工具。
52. “Highly Selective Photoelectroreduction of Carbon Dioxide to Ethanol over Graphene/Silicon Carbide Composites”, G Feng, S Wang, S. Li, R Ge, X Feng, J. Zhang, Y Song, X Dong, J Zhang, G Zeng, Q Zhang, G. Ma, Yi-De Chuang, X Zhang, J Guo, Y Sun*, W Wei*, W Chen*, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202218664.
doi.org/10.1002/ange.202218664
51. “Stille Type P–C Coupling Polycondensation towards Phosphorus-Crosslinked Polythiophenes with P-Regulated Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution”, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, X. Han, H. Chen, C. Xue, M. Peng, G. Ma* and Y. Ren*, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 2990-2998.
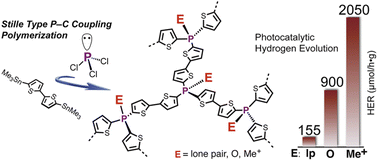
50. “Synthesis of Narrow-Band-Gap GaN:ZnO Solid Solution for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting”, K. Liu, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, W. Lin, J. Wang, Y. Xu, Y. Xiang, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, and G. Ma*, ACS Catal, 2022, 12(23), 14637–14646.
doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c04361

本工作通过在密封真空管中煅烧Ga2O3、Zn和NH4Cl的混合物合成了具有2.3 eV带隙的固溶体GaN:ZnO光催化剂,显著低于传统氨气氮化合成的2.7 eV。产物在牺牲试剂中具有较高的量子产率,同时在一步激发水分解中展现出高活性。使用GaN:ZnO作为析氧光催化剂,以SrTiO3:Rh作为析氢光催化剂构建Z-scheme整体水分解系统的太阳能-氢能转换效率可达3.7×10 -2 %,光化学稳定性长达100小时。
49. “Surface defects engineering of BiFeO3 films for improved photoelectrochemical water oxidation”, Z.Nie, X. Yan, B. Zhang, G. Ma*, N. Yang*, Ceramics International, 2022, 48(24), 36279-36286.
10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.08.187
48. “Insight into the Light-Driven Hydrogen Production over Pure and Rh-Doped Rutile in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid: Impact of Interfacial Chemistry on Photocatalysts”, J. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Tang, K. Liu, B. Zhang, and G. Ma*, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(30), 34656-34664.
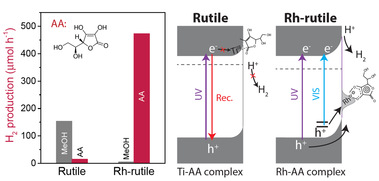
本研究发现纯Rutile相TiO2与Rh掺杂Rutile在两种不同牺牲试剂(甲醇和抗坏血酸)中的析氢能力存在本质上的差异。电容式表面光电压谱(SPS)表明Rh-rutile在两种牺牲试剂中,Rh介入所形成能带结构大幅促进了电荷分离。强度调制光电流谱(IMPS)测试发现,Rh-rutile在抗坏血酸溶液中能够形成Rh-AA表面键,并作为反应活性位点抑制光生电荷复合的发生。本工作从光电化学的角度深入理解了Rh掺杂表面化学状态对光催化反应的显著影响,阐明了抗坏血酸作为牺牲试剂测试材料性能的机理。
47. “Facet Engineering on WO3 Mono-Particle-Layer Electrode for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting”, W. Lin, B. Zhang, K. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Wang, G. Ma*, Chemistry-A European Journal,2022, 28(51), e202201169.
doi.org/10.1002/chem.202201169
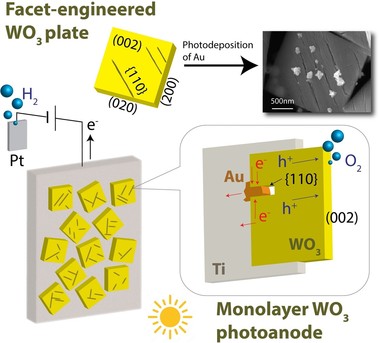
WO3光阳极的光电化学(PEC)性能很大程度上受晶面取向的影响。通过摩擦法得到沿 (002) 面高度均匀排列的单颗粒层WO3电极,提高了PEC水氧化动力学和稳定性。沿着表面形成的裂纹(即{110}面的边缘)光沉积填充Au可以进一步提高电子收集效率。这项工作为制备晶面选择性的WO3光电极提供了一条简便的途径,该方法也适用于其他具有各向异性电荷迁移的半导体光催化剂。
46. “Facet-Oriented Assembly of Mo:BiVO4 and Rh:SrTiO3 Particles: Integration of p–n Conjugated Photo-electrochemical System in a Particle Applied to Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting”, B. Zhang, K. Liu, Y. Xiang, J. Wang, W. Lin, M. Guo, G. Ma*, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 4, 2415–2425.
doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c00306
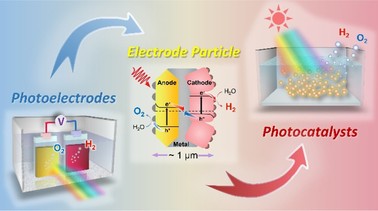
本工作将p-n共轭双电极水分解系统小型化为一个粒子(电极颗粒)用于光催化反应。将p型掺铑钛酸锶(Rh:SrTiO3)光电阴极材料选择性沉积在颗粒型掺钼钒酸铋(Mo:BiVO4)光电阳极的电子积累面上,并插入部分氧化的In@InOx中间层作为颗粒粘合剂和电荷导体。利用高效的界面电荷转移和有效的表面修饰,复合电极颗粒上实现了可见光驱动PC整体水分解为H2和O2。
45.“Formation of multifaceted nano-groove structure on rutile TiO2 photoanode for efficient electron-hole separation and water splitting”, X. Zhan, Y. Luo, Z. Wang, Y. Xiang, Z. Peng, Y. Han, H. Zhang, R. Chen, Q. Zhou, H. Peng, H. Huang, W. Liu, Ou X., G. Ma*, F. Fan*, F. Yang, C. Li, Z. Liu*, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 65, 19.
doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2021.05.007
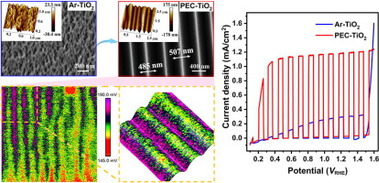
44. “Doping Rh into TiO2 as a visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: The difference between rutile and anatase”, J. Wang, K. Liu, B. Zhang, Y. Qiu, Y. Xiang, W. Lin, B. Yang, B. Li*, and G. Ma*, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 119, 213901.
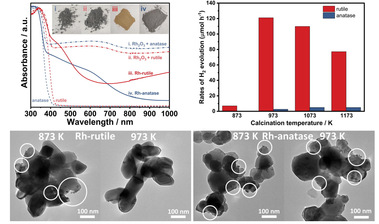
本文报道通过Rh的掺杂获得的窄带隙二氧化钛光催化剂对于Rutile和Anatase两种晶相有明显差异。实验发现Rh容易进入Rutile的晶体结构中,然而Rh以纳米氧化铑形式存在于Anatase相的表面。光催化结果显示在可见光照射下,以抗坏血酸为牺牲剂,Rh掺杂Rutile的析氢性能相较于Rh掺杂的Anatase有约50倍的提升。
43. “Fabrication of a facet-oriented BiVO4 photoanode by particle engineering for promotion of charge separation efficiency”, B. Zhang, Y. Xiang, M. Guo, J. Wang, K. Liu, W. Lin, and G. Ma*, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4, 4259.
doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.1c00694
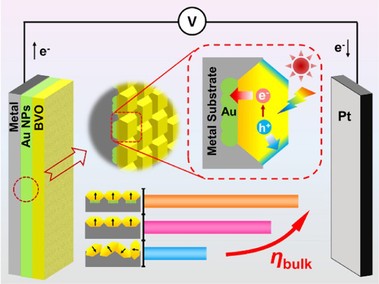
本工作通过 Langmuir-Blodgett技术组装单层十面体BiVO4 颗粒,使其(040)晶面朝向基板排列,并在PEC氧化反应中表现出比随机取向的电极更高的性能。在BiVO4和基板之间插入Au纳米颗粒作为电子传输层后,光电流进一步增强,表明晶体取向和电子传输隧道协同效应对BiVO4光阳极的活性起促进作用。
42. “Design and fabrication of Bi2O3/BiFeO3 heterojunction film with improvedphotoelectrochemical performance”, X. Yan, R. Pu, R. Xie, B. Zhang, Y. Shi, W. Liu*, G. Ma*, N. Yang*, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 552, 149442.
doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149442
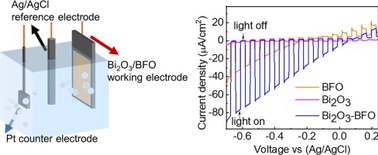
41. “Flux-assisted preparation of Sm2Ti2S2O5 powder applied to photocatalytic H2 production from water”, M. Chao, G. Ma*, Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2021, 36, 16.
doi.org/10.11862/CJIC.2021.006
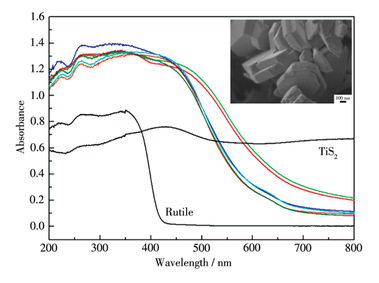
本工作使用TiO2、TiS2及Sm2O3作为前驱体,采用混合熔盐来降低合成温度,在较低温度下成功合成了具有低带隙的Sm2Ti2S2O5片状晶体颗粒。从XRD结果分析,证明了STSO的热力学结晶温度在520 ℃左右,远低于之前报道的650 ℃的最低合成温度。同一合成温度下,采用LiCl‑CsCl熔盐制备的STSO的厚度小于LiCl‑KCl所得产物。在可见光及含有Na2S‑Na2SO3空穴牺牲剂的溶液中,所制备的STSO颗粒表现出最高35 μmol·h-1的光催化分解水产氢活性以及20 h以上的产氢稳定性。
40. “Facet-selective construction of Cu2O/Pt/BiVO4 heterojunction arrays for photocatalytic H2 production from water”, J. Liu, B. Zhang, Y. Xiang, G. Ma*, New J. Chem, 2020, 45, 517.
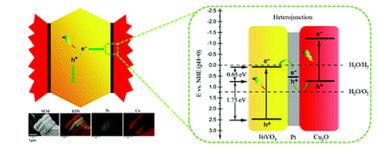
鉴于BiVO4颗粒在光激发下体相电子易于向{010}晶面定向传输,本工作通过光还原沉积方法依次将Pt和Cu2O纳米粒子沉积在十面体BiVO4颗粒上下平行的{010}晶面上,成功制备出具有规则三明治结构Cu2O/Pt/BiVO4异质结。其中金属 Pt 中间层有效促进电荷在异质结界面处的传输。
39. “A one-step synthesis of a Ta3N5 nanorod photoanode from Ta plates and NH4Cl powder for photoelectrochemical water oxidation”, Y. Xiang, B. Zhang, J. Liu, S. Chen, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, G. Ma*, Chem. Comm, 2020, 56, 11843.
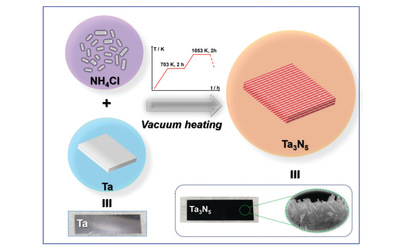
Ta3N5的禁带宽度为2.0 eV,对应15.9 %的理论太阳能制氢效率,具有非常好的应用前景。但Ta3N5的制备通常采用氨气高温氮化法,产物颗粒形貌不理想且氮转化率很低。本工作借助真空封管氮化的简单工艺,在以比文献低近200 K的加热温度以及更短的反应时间下制备出具有纳米棒状结构的Ta3N5/Ta薄膜光阳极。该电极表现出3.2 mA·cm-2光电流,产氧法拉第效率接近100 %。
38. “Alteration of onset potentials of Rh-doped SrTiO3 electrodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting”, M. Guo, G. Ma*, J. Cat., 2020, 391, 241.
doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2020.08.029
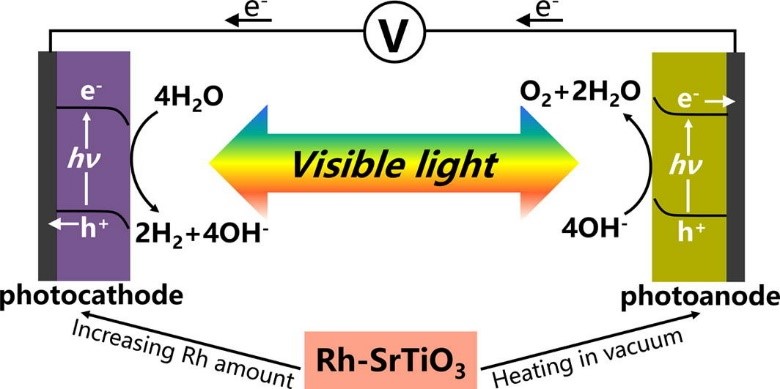
铑掺杂SrTiO3是一种可见光响应氧化物半导体光催化剂,可应用于全水分解。在本研究中,通过改变Rh掺杂量或通过真空加热处理调整Ti和Rh的元素比例及价态,成功地改变了这种材料的光阴极和光阳极特性,并实现了可见光驱动的低偏压光电化学水分解。
37. “Diatom-inspired multiscale mineralization of patterned protein-polysaccharide complex structures”, K. Li, Y. Li, X. Wang, M. Cui, B. An, J. Pu, J. Liu, B. Zhang, G. Ma, C. Zhong*, Natl. Sci. Rev., 2020.
36. “Efficient photoelectrochemical hydrogen production over CuInS2 photocathodes modified with amorphous Ni-MoSx operating in a neutral electrolyte”, J. Zhao, T. Minegishi, G. Ma, M. Zhong, T. Hisatomi, M. Katayama, T. Yamada, K. Domen*, Sustain. Energ. Fuels, 2020, 4, 1607.
35. “Metal selenides for photocatalytic Z-scheme pure water splitting mediated by reduced graphene oxide”, S. Chen, T. Hisatomi, G. Ma, Z. Wang, Z. Pan, T. Takata, K. Domen*, Chin. J. Cat., 2019, 40, 1668.
doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63326-7
34. “Visible‐light‐driven photocatalytic Z‐Scheme overall water splitting in La5Ti2AgS5O7‐based Powder‐suspension system”, Z. Song, T. Hisatomi, S. Chen, Q. Wang, G. Ma, S. Li, X. Zhu, S. Sun*, K. Domen*, ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 1906.
doi/full/10.1002/cssc.201802306
33. “Efficient hydrogen evolution on (CuInS₂)x(ZnS)1-x solid solution-based photocathodes under simulated sunlight”, J. Zhao, T. Minegishi, H. Kaneko, G. Ma, M. Zhong, M. Nakabayashi, M. Katayama, N. Shibata, T. Yamada, K. Domen*, Chem. Comm., 2019, 55, 470.
32. “Metal selenide photocatalysts for visible-light-driven Z-scheme pure water splitting”, S. Chen, G. Ma, Q. Wang, S. Sun, T. Hisatomi, T. Higashi, Z. Wang, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, Z. Pan, T. Hayashi, T. Minegishi, T. Takata, K. Domen*, J. Mat. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 7415.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA00768G
31. “Plate-like Sm2Ti2S2O5 particles prepared by a flux-assisted one-step synthesis for the evolution of O2 from aqueous solutions by both photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical reactions”, G. Ma, Y. Kuang, D. H. K. Murthy, T. Hisatomi, J. Seo, S. Chen, H. Matsuzaki, Y. Suzuki, M. Katayama, T. Minegishi, K. Seki, A. Furube, K. Domen*, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 13492.
http://doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12087
30. “Efficient redox-mediator-free Z-scheme water splitting employing oxysulfide photocatalysts under visible light”, S. Sun, T. Hisatomi, Q. Wang, S. Chen, G. Ma, J. Liu, S. Nandy, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama, K. Domen*, ACS Cat., 2018, 8, 1690.
http://doi/10.1021/acscatal.7b03884
Before Joining ShanghaiTech:
29. “Enhancement of the H2 evolution activity of La5Ti2Cu(S1−xSex)5O7 photocatalysts by coloading Pt and NiS cocatalysts”, S. Nandy, T. Hisatomi, G. Ma, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama, K. Domen*, J. Mat. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 6106.
28. “Ultrastable low-bias water spitting photoanodes via photocorrosion inhibition and in-situ catalyst regeneration”, Y. Kuang, Q. Jia, G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi, H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada, A. Kudo, K. Domen*, Nature Energy, 2017, 2, 16191.
27. “Visible light-driven Z-scheme water splitting using oxysulfide H2 evolution photocatalysts”, G. Ma, S. Chen, Y. Kuang, S. Akiyama, T. Hisatomi, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, M. Katayama, T. Minegishi, K. Domen*, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016,7, 3892.
26. “Rationalizing long-lived photo-excited carriers in photocatalyst (La5Ti2CuS5O7) in terms of one-dimensional carrier transport”, Y. Suzuki, R. Singh, H. Matsuzaki, A. Furube, G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, K. Seki*, Chem. Phys., 2016, 476, 9.
25. “Photoanodic and photocathodic behaviours of La5Ti2CuS5O7 electrodes in water splitting reaction”, G. Ma, Y. Suzuki, R. Singh, A. Iwanaga, Y. Moriya, T. Minegishi, J. Liu, T. Hisatomi, H. Nishiyama, M. Katayama, K. Seki, A. Furube, T. Yamada, K. Domen*, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 4513.
24. “Site-selective photodeposition of Pt on a particulate Sc-La5Ti2CuS5O7 photocathode: evidence for one-dimensional charge transfer”, G. Ma, J. Liu, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi, Y. Moriya, M. Iwase, H. Nishiyama, M. Katayama, T. Yamada, K. Domen*, Chem. Comm., 2015, 51, 4302.
23. “Enhancement of solar hydrogen evolution from water by surface modification with CdS and TiO2 on porous CuInS2 photocathodes prepared by electrodeposition-sulfurization method”, J. Zhao, T. Minegishi, L. Zhang, M. Zhong, Gunawan, M. Nakabayashi, G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, M. Katayama, S. Ikeda*, N. Shibata, T. Yamada, K. Domen*, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 11808.
22. “Improving the photoelectrochemical activity of La5Ti2CuS5O7 for hydrogen evolution by particle transfer and doping”, J. Liu, T. Hisatomi, G. Ma, A. Iwanaga, T. Minegishi, Y. Moriya, M. Katayama, J. Kubota, K. Domen*, Energ. Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 2239.
21. “Fabrication of photocatalyst panels and the factors determining their activity for water splitting”, A. Xiong, G. Ma, K. Maeda, T. Takata, T. Hisatomi, T. Setoyama, J. Kubota, K. Domen*, Cat. Sci. Tech., 2014, 4, 325.
20. “Photoelectrochemical conversion of toluene to methylcyclohexane as an organic hydride by Cu2ZnSnS4‐based photoelectrode assemblies”, P. Wang, T. Minegishi, G. Ma, K. Takanabe, Y. Satou, S. Maekawa, Y. Kobori, J. Kubota, K. Domen*, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 2469.
19. “Semiconductor monolayer assemblies with oriented crystal faces”, G. Ma, T. Takata, M. Katayama, F. Zhang, Y. Moriya, K. Takanabe, J. Kubota, K. Domen*, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 59.
18. “A hybrid photocatalytic system comprising ZnS as light harvester and an [Fe2S2] hydrogenase mimic as hydrogen evolution catalyst”, F. Wen, X. Wang, L. Huang, G. Ma, J. Yang, C. Li*, Chemsuschem,2012, 5, 849.
17. “Photoelectrochemical hydrogen production on Cu2ZnSnS4/Mo-mesh thin-film electrodes prepared by electroplating”, G. Ma, T. Minegishi, D. Yokoyama, J. Kubota, K. Domen*, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2011, 501, 619.
16. “Photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS loaded with WS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation”, X. Zong, J. Han, G. Ma, H. Yan, G. Wu and C. Li*, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 12202.
15. “Enhanced visible-Light activity of titania via confinement inside carbon nanotubes”, W. Chen*, Z. Fan, B. Zhang, G. Ma, K. Takanabe, X. Zhang, Z. Lai*, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 14896.
14. “Photocatalytic H2 evolution on MoS2/CdS catalyst under visible light irradiation”, X. Zong, G. Wu, H. Yan, G. Ma, J. Shi, F. Wen, L. Wang, C. Li*, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 1963.
13. “H2 evolution from water on modified Cu2ZnSnS4 photoelectrode under solar light”, D. Yokoyama, T. Minegishi, K. Jimbo, T. Hisatomi, G. Ma, M. Katayama, J. Kubota, H. Katagiri, K. Domen*, Appl. Phys. Express, 2010, 3, 101202.
12. “Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic performance of Zn2-xGeO4-x-3yN2y catalysts under visible light irradiation”, B. Ma, X. Zong, G. Ma, J. Yang, P. Ying, C. Li*, Chem. Bull., 2010, 6, 556.
11. “Photocatalytic hydrogen production on CuInS2-ZnS solid solution prepared by solvothermal method”, G. Ma, Z. Lei, H. Yan, X. Zong, C. Li*, Chin. J. Cat., 2009,30, 73.
10. “Visible-light-driven hydrogen production with extremely high quantum efficiency on Pt–PdS/CdS photocatalyst”, H. Yan, J. Yang, G. Ma, G. Wu, X. Zong, Z. Lei, J. Shi, C. Li*, J. Cat., 2009, 266, 165.
9. “Visible light driven H2 production in molecular systems employing colloidal MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst”, X. Zong, Y. Na, F. Wen, G. Ma, J. Yang, D. Wang, Y. Ma, M. Wang, L. Sun, C. Li*, Chem. Comm., 2009, 30, 4536.
8. “Direct splitting of H2S into H2 and S on CdS-based photocatalyst under visible light irradiation”, G. Ma, H. Yan, J. Shi, X. Zong, Z. Lei, C. Li*, J. Cat., 2008, 260, 134.
7. “Photocatalytic splitting of H2S to produce hydrogen by gas-solid phase reaction”, G. Ma, H. Yan, X. Zong, B. Ma, H. Jiang, F. Wen, C. Li*, Chin. J. Cat., 2008, 29, 313.
6. “Enhancement of photocatalytic H2evolution on CdS by loading MoS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation”, X. Zong, H. Yan, G. Wu, G. Ma, F. Wen, L. Wang, C. Li*,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 7176.
5. “Suppressing the CO formation via anion adsorption on Pt/TiO2 for the H2 production from the photocatalytic reforming of methanol”, G. Wu, T. Chen, X. Zong, H. Yan, G. Ma, C. Li*, J. Cat., 2008, 253, 225.
4. “Kinetics of photogenerated electrons involved in photocatalytic reaction of methanol on Pt/TiO2”, T. Chen, G. Wu, Z. Feng, J. Shi, G. Ma, P. Ying, C. Li*, Chin. J. Chem. Phys., 2007, 20, 483.
3. “Mechanistic studies of photocatalytic reaction of methanol for hydrogen production on Pt/TiO2 by in-situ FTIR and time-resolved IR spectroscopy”, T. Chen, Z. Feng, G. Wu, J. Shi, G. Ma, P. Ying, C. Li*, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 8005.
2. “Sulfur-substituted and zinc-doped In(OH)3: A new class of catalyst for photocatalytic H2production from water under visible light illumination”, Z. Lei, G. Ma, M. Liu, W. You, H. Yan, G. Wu, T. Takata, M. Hara, K. Domen*, C. Li*, J. Cat., 2006, 237, 322.
1. “Water reduction and oxidation on Pt–Ru/Y2Ta2O5N2 catalyst under visible light irradiation”, M. Liu, W. You, Z. Lei, G. Zhou, J. Yang, G. Wu, G. Ma, G. Luan, T. Takata, M. Hara, K. Domen*, C. Li*, Chem. Comm., 2004, 36, 2192.
Book chapter:
G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, “Semiconductors for Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Solar Water Splitting”, in “From Molecules to Materials-Pathway to Artificial Photosynthesis”, Springer Publisher, 2015, pp 1-56, ISBN 978-3-319-13800-8.
Patents:
马贵军; 向遥,一种含氮化合物的制备方法,ZL 201910687950.9
马贵军; 王佳明,一种单原子铑催化剂及其制备方法和应用,ZL 202111231496.X
马贵军; 张博杨,一种具有统一晶面取向特性晶体粒子电极的制备方法,ZL 202110285246.8
马贵军; 刘铠玮,一种基于GaN:ZnO固溶体的Z型光催化分解水反应体系的构建方法及其应用,ZL 202210845682.0
Orcid and ResearcherID:
https://www.scopus.com/authid/detail.uri?authorId=24280560300
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7943-9750
https://publons.com/researcher/1677607/guijun-ma/
| 组内活动(Activities) |
|

25年9月,第18届全国太阳能光化学与光催化学术会议

25年7月,欢送毕业生张家铭,许垚
2024年11月,上海野生动物园 2024年7月,欢送24届毕业生刘铠玮,汤业成
2024年7月,欢送24届毕业生刘铠玮,汤业成 2023年11月,中共一大会址
2023年11月,中共一大会址 2022年11月,海昌海洋公园
2022年11月,海昌海洋公园

2020年10月合照

第16届全国太阳能光化学与光催化学术会议
欢送郑仓晟工程师 |
| 组内动态(News) |
|
应聘者请通过电子邮件联系马贵军老师magj@shanghaitech.edu.cn, 欢迎感兴趣的学生学者们加盟本课题组! |
|
 | 张继方 / 助理研究员 (2021)PhD: 2015-2019, 巴斯大学, 化学工程 Email:zhangjf3@shanghaitech.edu.cn |
| 史珂 / 博士研究生(2020)BS: 2016-2020, 上海师范大学, 化学工程与工艺Email:shike@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 张自豪 / 博士研究生 (2021)BS: 2017-2021, 中国矿业大学, 材料学 Email:zhangzh5@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 王海峰 / 博士研究生 (2022)BS: 2018-2022, 东北师范大学, 化学 Email:wanghf2022@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 刘梦 / 博士研究生 (2022)BS: 2018-2022, 青岛科技大学, 新能源材料与器件 Email:liumeng2022@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 李呈卓 / 硕士研究生 (2023)BS: 2017-2021, 合肥工业大学, 化学工程与技术 Email:lichzh2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 叶一敏 / 硕士研究生 (2023)BS: 2017-2021, 郑州大学, 化学 Email:yeym2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 陶骁伟 / 博士研究生 (2024)BS: 2020-2024, 上海科技大学, 材料科学与工程 Email:taoxw @shanghaitech.edu.cn Tel:021-20685277 |
| 毕业学生/前组员(Alumni) |
|
工作人员:
仇亚茹 / 博士后 (2020)
郑仓晟 / Lab Engineer(2018)
博士毕业生:
张家铭(2025届)
许垚 (2025届)
刘铠玮(2024届)
张博杨(2023届)
硕士毕业生:
汤业成 (2024届)
林文瑞 (2022届)
王佳明 (2022届)
向遥 (2022届)
刘金涛 (2021届)
郭美 (2020届)
晁明坤 (2020届)
本科毕业生:
陶骁伟/ 上科大本科生(2024届)
汤业成/ 上科大本科生(2021届)
许垚 / 上科大本科生(2020届)
陈奕璇/ 上科大本科生(2020届)
林文瑞/ 上科大本科生(2019届)
王嘉豪/ 上科大本科生(2019届)
杨懿 / 上科大本科生(2019届)
交换/访问生:
贾林虎/ 硕士研究生(2022年)
茅学曼/ 硕士研究生(2021年)
周伟成/ 硕士研究生(2018年)