2025 Junhan Xie, Di Li, Haozheng Li, Bo Peng, Qinye Bao, Jiaming Jiang*, Bo Li*, Weimin Liu*, Surface and Bulk Defect Passivation in MAPbI3 Perovskites with Daminozide: Effects on Carrier Dynamics and Mobility. Adv, Sci. 2025 , 202500530.
Z Wang‡, Y Chen‡, J Jiang, X Zhao,W Liu*. Mapping photoisomerization dynamics on a three-state model potential energy surface in bacteriorhodopsin using femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. Chemical Science, 2025. 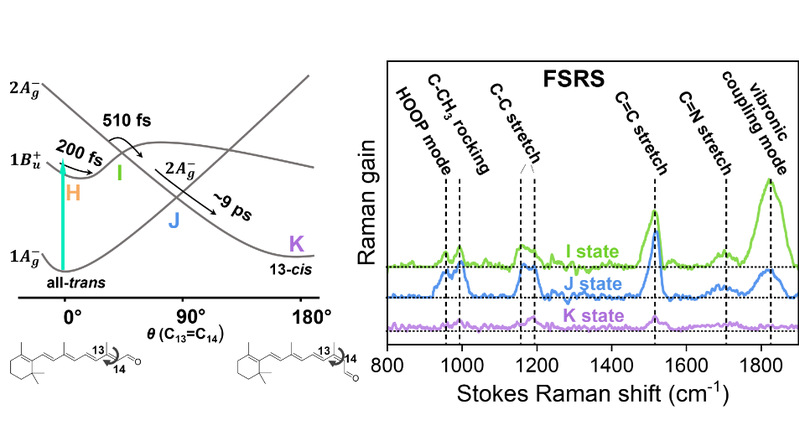
C Wang, Y Chen, P Suo, K Sun, S Wang, X Lin, W Liu*, G Ma*. Gate-Controlled Ultrafast Interlayer Carrier Flow in Gr/MoS2 Heterostructures. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2025. 
T Ma, M Ruan, R Zhao, Z Wang, Y Wang*, Y Huang*, Y Weng*, W Liu*. Distorted Intermediate SX (1Bu–) State in Xanthophylls Drives Efficient Energy Transfer in Light-Harvesting Complex II. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2025. 
Y Chen, Z Wang, J Jiang*, W Liu*. Resolving Dual Photoreaction Channels of All-Trans-Retinal Using Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2025. 
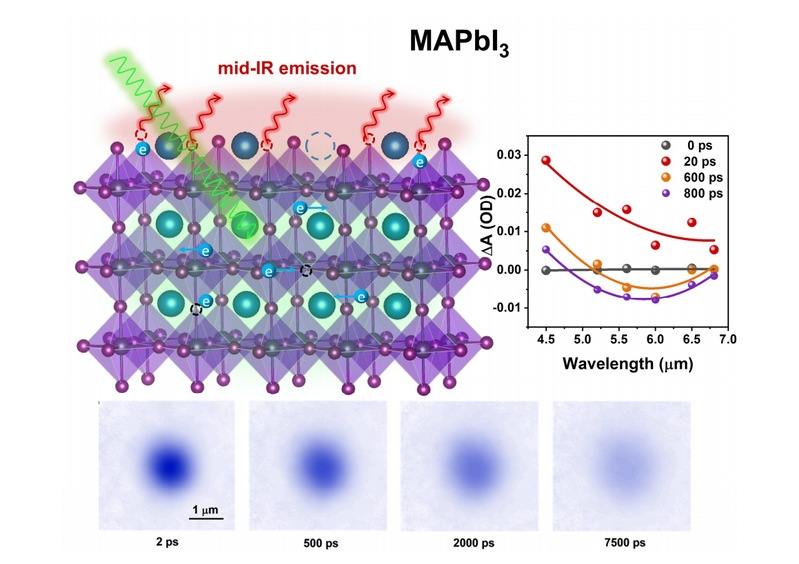
Di Li, Junhan Xie, Shaobing Xiong, Xiaoxiao Zang, Zhennan Lin, Yuning Wu, Weimin Liu*, Bo Li*, Zhenrong Sun, Junhao Chu, Qinye Bao*. Unveiling Charge Transfer and Recombination Dynamics in 3D/2D Heterostructure via Ultrafast Spectroscopy for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Sci. 2025, e08123. 2024 Wei, X.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Ji, Q*.; Liu, W*., Unveiling Spatiotemporal Diffusion of Hot Carriers Influenced by Spatial Nonuniform Hot Phonon Bottleneck Effect in Monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2024.
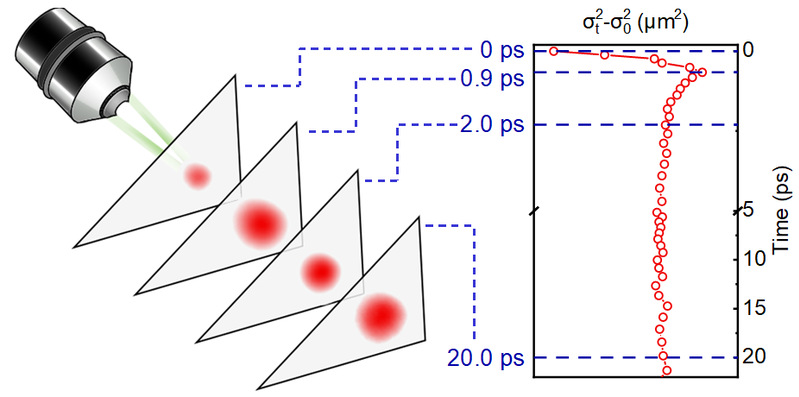
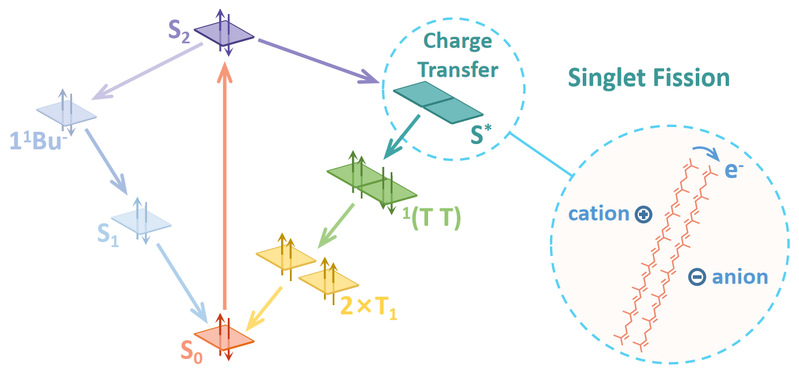
J. Xie, W. Zhou, H. Li, Z. Wang, J. Jiang, Y. Zhang, X. Shen, Z. Ning, W. Liu, Visualizing Carrier Diffusion in Cs-Doping FAPbI3 Perovskite Thin Films Using Transient Absorption Microscopy. Adv. Optical Mater. 2024, 12, 2303004. Peng, B., Wang, Z., Jiang, J., Huang, Y., & Liu, W. Investigation of ultrafast intermediate states during singlet fission in lycopene H-aggregate using femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2024; 160 (19): 194304.
Wang, C., Chen, Y., Xiong, R., Sun, K., Lin, X., Wang, W., Suo, P., Liu, W., & Ma, G. Weakening of the Many-Body Interactions Induced by Charge Transfer in Gr/WS2 Heterostructures.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C.2024 128 (22), 9209-9216
2023
Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, J.; Weng, T.; Ji, Q*.; Huang, Y*.; Fang, C*.; Liu, W*., Mapping the Complete Photocycle that Powers a Large Stokes Shift Red Fluorescent Protein. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 20233,135, e2022 
An, Q.; Xing, Y.; Pu, R.; Jia, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, A.; Zhang, S.; Yu, N.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J*.; Liu, W*.; Hong, X*.; Zuo, Z*.; Identification of alkoxy radicals as the hydrogen atom transfer agents in the Ce-catalyzed C–H functionalization. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2023,145, 1, 359–376 Pu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, J.; Weng, T.-C.; Huang, Y*.; Liu, W*., Investigation of Ultrafast Configurational Photoisomerization of Bilirubin Using Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2023, 14 (3), 809-816. 
Zhao, Z.; Pu, R.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Liu, W*., Identification of Ultraviolet Photoinduced Presolvated Electrons in Water as the Reducing Agent in the Photoreduction of Graphene Oxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2023. 
Lin, Y.; Wei, X.; Fang, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, W. Investigation of Ultrafast Photoisomerization Dynamics of Azobenzene Derivative (E)-1-Phenyl-2-((triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl)diazene†. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics , 2023, 36(6): 664-670.
| 2022
Suo, P.; Yan, S.; Pu, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Fu, J.; Lin, X.; Miao, F.; liang, S.; Liu, W*.; Ma, G.-H*., Ultrafast photocarrier and coherent phonon dynamics in type-Ⅱ Dirac semimetal PtTe2 thin films probed by optical spectroscopy. Photonics Research 2022. Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y*.; Liu W*., Tracking Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer and Isomerization Dynamics in 9- (2,2- Dicyanovinyl) Julolidine Using Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics 2022. Li, J.; Pu, R.; He, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, W*.; Li, J*., A Precipitation-Enhanced Emission (PEE) Strategy for Increasing the Brightness and Reducing the Liver Retention of NIR-II Fluorophores. Small 2022, 2204153.

| 2021
Wei, J.; Wu, Y.; Pu, R.; Shi, L.; Jiang, J.; Du, J.; Guo, Z*.; Huang, Y*.; Liu, W*., Tracking Ultrafast Structural Dynamics in a Dual-Emission Anti-Kasha-Active Fluorophore Using Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2021 , 12, 4466-4473. 
Xu, W., Wei, L., Wang, Z., Zhu, R., Jiang, J., Liu, H., Du, J., Weng, T. C., Zhang, Y. B*., Huang, Y*., & Liu, W*. (2021). Tracking Ultrafast Fluorescence Switch-On and Color-Tuned Dynamics in Acceptor-Donor-Acceptor Chromophore. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 125(38), 10796–10804. 
Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Kong, J.; Niu, X.; Chan, J. M*.; Liu, W*.; Xia, A*., Direct Tracking Excited-State Intramolecular Charge Redistribution of Acceptor–Donor–Acceptor Molecule by Means of Femtosecond Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2021. Ma, Q. S., Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Pu, R.; Ju, C.-W.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z*.; Liu, W*.; Li, R., Hot Carrier Transfer in a Graphene/PtSe2 Heterostructure Tuned by a Substrate-Introduced Effective Electric Field. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2021. Yan, X.; Pu, R.; Xie, R.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Liu, W*.; Ma, G*.; Yang, N*., Design and fabrication of Bi2O3/BiFeO3 heterojunction film with improved photoelectrochemical performance. Applied Surface Science 2021,552, 149442. Wang T, Wang S*, Liu Z, He Z, Yu P, Zhao M, Zhang H, Lu L, Wang Z, Wang Z, Zhang W*, Fan Y, Sun C, Zhao D, Liu W, Bünzli JG, Zhang F*. A hybrid erbium(III)-bacteriochlorin near-infrared probe for multiplexed biomedical imaging. Nat Mater. 2021 Nov;20(11):1571-1578. Zhang, P.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, D.; Liu, W.; Mai, Y*., Porphyrin-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymer Tubes: Template-Free Synthesis and A Photocatalyst for Visible-Light-Driven Thiocyanation of Anilines., Macromolecules 2021 54 (7), 3543-3553 Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Wei, J.; Jiang, J.; Du, J.; Li, B*.; Liu, W*., Investigation of multiphoton pumped stimulated emission in semiconductor material using femtosecond two pulses induced stimulated emission technique. Optics Communications 2021,479, 126446. Liu Z, Hu M, Du J*, Shi T, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Hu Z, Zhan Z, Chen K, Liu W, Tang J, Zhang H*, Leng Y*, Li R. Subwavelength-Polarized Quasi-Two-Dimensional Perovskite Single-Mode Nanolaser. ACS Nano. 2021 Apr 27;15(4):6900-6908. Yang Z, Yang K, Wei X, Liu W, Gao R, Jäkle F, Loo YL, Ren Y*. A Multiple Excited-State Engineering of Boron-Functionalized Diazapentacene Via a Tuning of the Molecular Orbital Coupling. J PhysChem Lett. 2021 Sep 30;12(38):9308-9314. Wei, Z.; Andong, X.; Jie, K.; Wenqi, X.; Xinmiao, N.; Di, S*.; Weimin, L*.; Andong, X*. Probing the Effect of Solvation on PhotoexcitedQuadrupolar Donor-Acceptor-Donor Molecule via Ultrafast Raman Spectroscopy. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics 2021
| 2020
An, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Pan, H.; Liu, W*.; Zuo, Z*., Cerium-Catalyzed C–H Functionalizations of Alkanes Utilizing Alcohols as Hydrogen Atom Transfer Agents. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2020,142 (13), 6216-6226. Fu, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Liu, W*.; Chen, J*.; Xu, J., Observation of triplet nπ* state in ultrafast intersystem crossing of 6-azathymine. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 2020,396, 112491. Shi, L.; Yan, C.; Guo, Z*.; Chi, W.; Wei, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, X*.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W.-H*., De novo strategy with engineering anti-Kasha/Kasha fluorophores enables reliable ratiometric quantification of biomolecules. Nature Communications 2020,11 (1), 1-11.
王子钰; 魏景乐; 徐文琪; 姜甲明; 黄逸凡*; 刘伟民*, 利用飞秒受激拉曼光谱技术研究 Pyranine 分子激发态质子传递过程. 物理学报 2020,69 (19), 198201-1-198201-8.
| 2019 Shang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, B.; Ke, Y.; Liu, W*.; Ning, Z*., Highly stable hybrid perovskite light-emitting diodes based on Dion-Jacobson structure. Science advances 2019, 5 (8), eaaw8072. (co-corresponding author) Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Suo, P.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Lin, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, W*.; Ma, G*., Optically controlled ultrafast terahertz switching in a CdTe nanostructure thin film. Applied optics 2019, 58 (30), 8200-8206. (co-corresponding author) Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y. M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, T*., Ultrafast self-trapping of photoexcited carriers sets the upper limit on antimony trisulfide photovoltaic devices. Nature communications 2019,10 (1), 1-8.
| 2018及以前 Liu, W.; Tang, L.; Oscar, B. G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Fang, C*., Tracking ultrafast vibrational cooling during excited-state proton transfer reaction with anti-Stokes and Stokes femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. The journal of physical chemistry letters 2017,8 (5), 997-1003. Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Oscar, B. G.; Zhu, L.; Fang, C*., Panoramic portrait of primary molecular events preceding excited state proton transfer in water. Chemical science 2016,7 (8), 5484-5494. Oscar, B. G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Campbell, R. E.; Fang, C*., Excited-state structural dynamics of a dual-emission calmodulin-green fluorescent protein sensor for calcium ion imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111 (28), 10191-10196. Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Chang, I.-Y.; Wills, L. A.; Zakharov, L. N.; Boettcher, S. W.; Cheong, P. H.-Y*.; Fang, C*.; Keszler, D. A*., Electrolytic synthesis of aqueous aluminum nanoclusters and in situ characterization by femtosecond Raman spectroscopy and computations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110 (46), 18397-18401.
| |
|
|
国家自然科学基金面上项目:《利用新型的飞秒受激拉曼光谱研究荧光蛋白的超快结构动力学》——已结题。 上海科技大学-上海光机所超强超短激光应用联合实验室平台建设项目:《面向先进材料的超快光谱实验平台》 上海市自然科学基金资助项目:《利用飞秒受激拉曼光谱研究可逆光学开-关荧光蛋白的激发态结构动力学》
|
|


















